|
Broadband Monitor
|
|
The Broadband Monitor lets you quickly tell if your broadband connection is working. By running regular checks you can tell if your connection is up and if your connection speed is normal. It can run in the background from the system tray to monitor your connection.
|
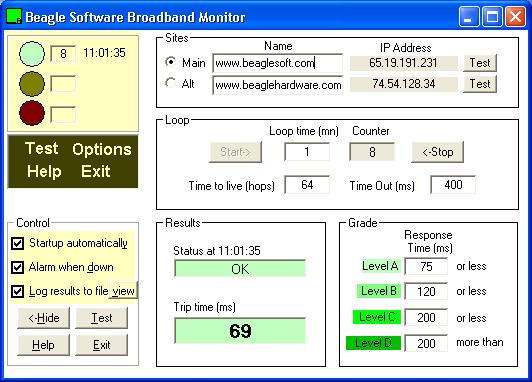
Broadband Monitor screen
Features
• Checks broadband connection by pinging remote Internet sites.
• Shows the relative connection speed with a 4 level grading scheme.
• Small, light application runs in the task bar.
• Can write results to log file
• Can also be used to monitor LAN/WAN connectivity or to monitor a specific computer or web site.
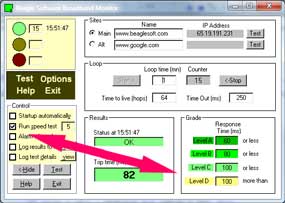
The main monitor screen is divided into 6 sections:
Indicator
Sites
Loop
Results
Grade
Control
| Main Indicator
Shows the results of the last test
(green=pass, yellow=failed last test, red=failed repeatedly), the number
of times each test result has happened and the time of the last test
result at level. |
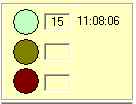 |
The box at right shows that the test has passed 15 times and the
last passed test was at 11:08 AM. Note that a response from the site within
the timeout period is considered a pass, regardless of the grade.
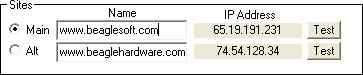
Main/Alt
Primary
and secondary sites used fro testing. This can be web sites, computers on a LAN or an IP address.
Name
Name of the web site or computer. This is the name that will be resolved to an IP address and used for testing
IP Address
This is the IP address resolved from the name.
Test
Press test button to check the connectivity.
| Loop Section
Tells how often to check the connection. The test uses Ping to test the
connection and measure the connection speed.
|
 |
Start/Stop
Starts/Stops the test
loop.
Loop Counter
Counts how many times the test has been completed.
Loop time
Time, in minutes,
between each test.
Time to Live:
Maximum number of hops
allowed to destination. The default TTL value is 64 hops. We recommend changing this to 128 if you have difficulty reaching certain sites.
Time-to-live (TTL) is a value in an Internet Protocol (IP) packet that tells a network router whether or not the packet has been in the network too long and should be discarded. For a number of reasons, packets may not get delivered to their destination in a reasonable length of time. For example, a combination of incorrect routing tables could cause a packet to loop endlessly. A solution is to discard the packet after a certain time and send a message to the originator, who can decide whether to resend the packet. The original idea of TTL was that it would specify a certain time span in seconds that, when exhausted, would cause the packet to be discarded. Since each router is required to subtract at least one count from the TTL field, the count is usually used to mean the number of router hops the packet is allowed before it must be discarded. Each router that receives a packet subtracts one from the count in the TTL field. When the count reaches zero, the router detecting it discards the packet and sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) message back to the originating host.
Time Out
Maximum time to wait for a reply from the site, in milliseconds.
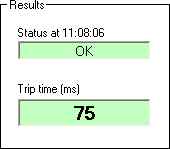
Status at …
Shows OK if passes test, otherwise shows error.
Trip Time
Shows the round trip time (in milliseconds) of a successful ping.
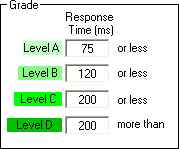
| Grade Section
The grade section allows you to color code the results of the successful test. The speed of the response can be compared against 4 different levels, each identified with a shade of green. Remember that lower numbers indicate a faster connection.
The default value of level A, 75 ms, means that a site responding in 75 ms
or less will be considered the fastest. |
 |
| Control Section
Control how the monitor will
function
|
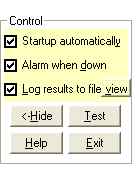
Controls, Lite Version
|
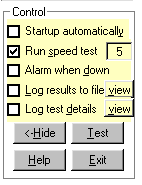
Controls, Full Version |
Startup Automatically
Check this if you want Broadband monitor to start up every time you log in to Windows. The monitor will be added to the system tray and will start automatically.
Alarm when down
Beeps whenever a test
fails. Useful in drawing attention to a bad connection or a downed site.
Run Speed Test
(full version)
Checks that the round
trip time is within a set time. Uses level D as a cutoff value when
evaluating results. Includes a threshold value to re-try test a set number
of times before throwing error.
The Speed Test Uses the Level D Setting
as the Speed Limit
You can change the
maximum allowable round trip time in the Level D box and set the number of
allowable failures before alarming in the box next to the check box.
Log Results to File
Check this if you want
Broadband monitor to log results to a text file, bblogfile.txt . A log entry is created whenever there is a change in connection status.
View -
displays the log file using notepad.
Log Test Details
(full version)
Check this if you want Broadband monitor to log
the results of each test into a file, bbdetail.csv, A log entry is created whenever there is a change in connection status.
View -
displays the log file using notepad. The file can also be
opened and viewed by a spreadsheet program such as Microsoft Excel.
Location of log files:
On early versions of Windows (thru XP) the log files can be found in the same directory as broadband monitor.
On later version of Windows it will be found in the common data directory (i.e.
C:\ProgramData\BroadbandMon\) You can view the header in the Log Results file to
see the location of the file on your computer.
Log File Format
Result Log, file
name: bblogfle.txt
The result log shows every time the state of the connection changes (i.e.
Start, Failed, Connect)
File Format:
Header: Beagle Software Broadband Monitor log file: <complete path
of log file>
Body: <mm-dd-yy hh:nn:ss> , <status change message>
Example:
Beagle Software Broadband
Monitor log file: C:\ProgramData\BroadbandMon\bblogfle.txt
03-04-15 10:42:15 monitor starting...
03-04-15 11:46:55 connection to www.beaglesoft.com slowed
03-04-15 12:51:48 connection to www.beaglesoft.com slowed
Detail Log, file name
bbdetail.csv
The detail log saves the result of each test run. It includes the time
test was run, the IP address of the site contacted, the round trip time of the
test (if completed), the state and the result.
File Format:
Header: Date/Time , URL , Time ,
State , Result
Body: <mm-dd-yy hh:nn:ss> , <IP Addr> , <Trip Time ms>
, <Current State> , <Result>
Example:
Date/Time,URL,Time,State,Result
03-04-15 11:53:54,65.19.191.231,40,OK,OK
03-04-15 11:54:50,65.19.191.231,58,OK,OK
03-04-15 11:56:56,65.19.191.231,76,OK,Slow 1
03-04-15 11:57:52,65.19.191.231,78,OK,Slow 2
03-04-15 11:58:48,65.19.191.231,78,OK,Slow 3
03-04-15 11:59:44,65.19.191.231,77,OK,Slow 4
03-04-15 12:00:40,65.19.191.231,77,OK,Slow 5
03-04-15 12:01:36,65.19.191.231,75,Warning,Slowed
The format of the file is
comma delimited and can be opened directly by a spreadsheet program such as
Microsoft Excel.
Buttons
Contains the control buttons .
Test
Runs a test with the current settings.
Options
Exposes the test options
Help
For help.
Exit
Exit program (or returns to system tray).
Broadband Monitor
Home
About Broadband Monitor
Troubleshooting